About MOCAT2
MOCAT2 has been developed at EMBL to process large metagenomic datasets. But can of course also process small datasets. ;)
Please read the full MOCAT (v1.0) article at PLoS ONE or the PDF version.
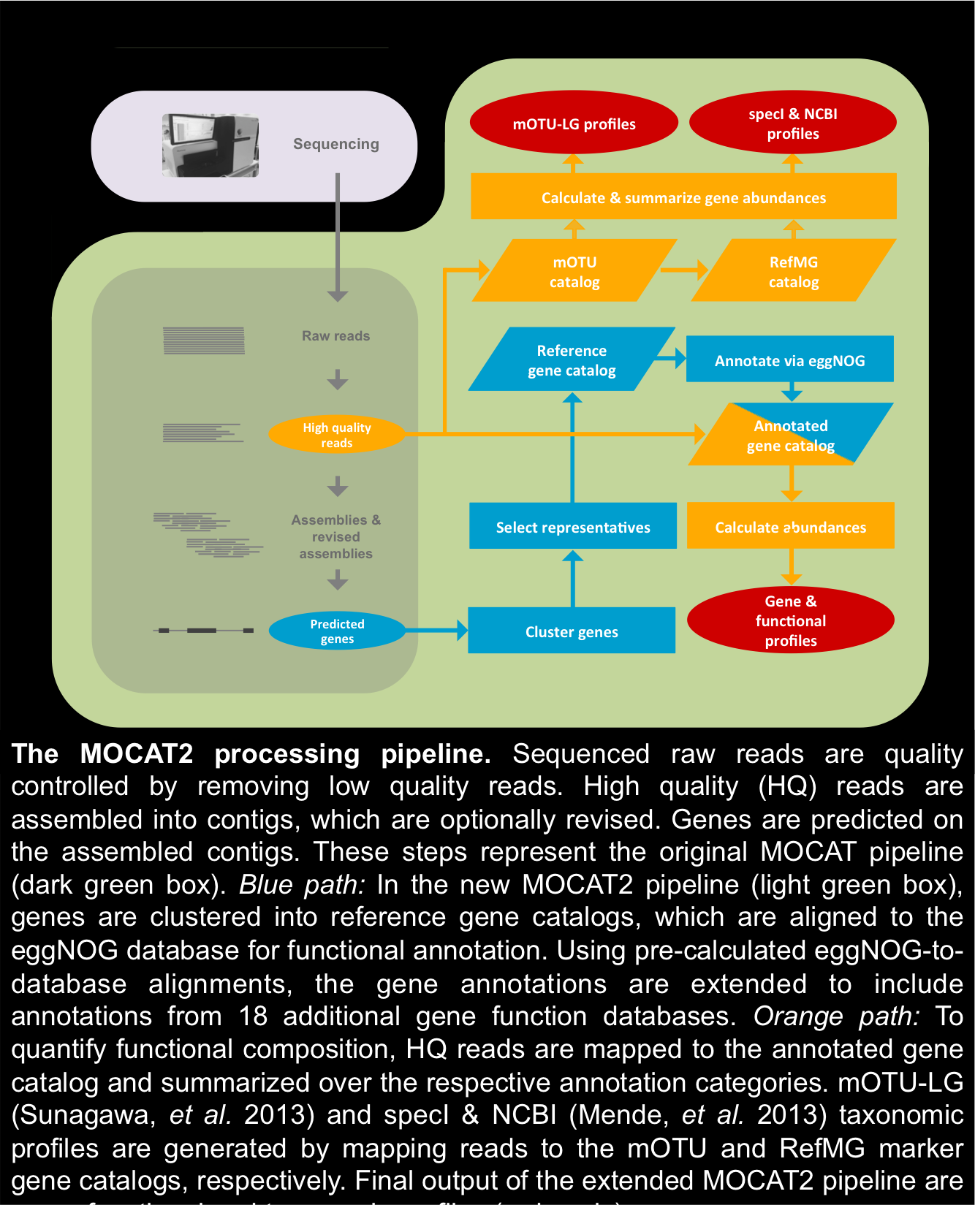
Processing steps, supported software & ubtegraedt databases:
Quality trimming and filtering of reads
- 3' trimming: FastX and SolexaQA
- 5' trimming: internal scripts
Screen or extract reads against a custom database
- SOAPaligner v2.21
Screen or extract reads against a custom FASTA file
- USEARCH v5/v6
Map reads to a reference database, estimate taxonomic/functional abundance
- SOAPaligner v2.21
- Internal scripts
Assemble high quality reads into contigs and scaftigs
- SOAPdenovo v1.05/v1.06
Revise the assemblies by correcting for indels and chimeric regions
- SOAPdenovo v1.05/v1.06 and BWA v0.7.5a-r16
Predict genes on assembles or revised contigs or scaftigs
- Prodigal v2.60
- MetaGeneMark v2.8
Extract single copy marker genes
- fetchMG v1.0
Cluster genes into reference gene catalogs
- CD-HIT v4.6
Annotate reference gene catalogs
- DIAMOND v0.7.9.58
- The filterBlastReport.pl script from SmashCommunity 1.6
Taxnomic databased integrated in MOCAT2
mOTU-LG: Sunagawa,S. et al. (2013) Metagenomic species profiling using universal phylogenetic marker genes. Nat. Methods, 10, 1196–9
specI & NCBI: Mende,D.R. et al. (2013) Accurate and universal delineation of prokaryotic species. Nat. Methods, 10, 881–4.
Pre-compiled reference gene catalogs compatible with MOCAT2
IGC (human gut): Li,J. et al. (2014) An integrated catalog of reference genes in the human gut microbiome. Nat. Biotechnol., 32, 834–41.
CRC-RGC (human gut): Zeller,G. et al. (2014) Potential of fecal microbiota for early-stage detection of colorectal cancer. Mol. Syst. Biol., 10, 766.
skin-RGC (human skin): Oh,J. et al. (2014) Biogeography and individuality shape function in the human skin metagenome. Nature, 514, 59–64.
mouse-RGC (human skin): Xiao,L. et al. (2015) A catalog of the mouse gut metagenome. Nat Biotech, 33, 1103–1108.
OM-RGC (ocean): Sunagawa,S. et al. (2015) Structure and function of the global ocean microbiome. Science, 348 (6237), 1:10
Functional ddatabases integrated in MOCAT2
eggNOG: Huerta-Cepas, J., et al. eggNOG 4.5: a hierarchical orthology framework with improved functional annotations for eukaryotic, prokaryotic and viral sequences. Nucleic Acids Res 2015. 10.1093/nar/gkv1248.
ARDB: Liu,B. and Pop,M. (2009) ARDB—Antibiotic Resistance Genes Database. Nucleic Acids Res. , 37 , D443–D447.
CARD: McArthur, A.G., et al. The comprehensive antibiotic resistance database. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 2013;57(7):3348-3357. 10.1128/AAC.00419-13.
DBETH: Chakraborty, A., et al. DBETH: a Database of Bacterial Exotoxins for Human. Nucleic Acid Res. 2012;40 Database issue):D615-20 0.1093/nar/gkr942
dbCAN: Yin, Y., et al. dbCAN: a web resource for automated carbohydrate-active enzyme annotation. Nucleic Acids Res 2012;40(Web Server issue):W445-451. 10.1093/nar/gks479.
DrugBank: Knox C., et al. DrugBank 3.0: a comprehensive resource for 'omics' research on drugs. Nucleic Acids Res 2011;39(Database issue):D1035-41. 10.1093/nar/gkq1126
ICEberg: Bi D., et al. ICEberg: a web-based resource for integrative and conjugative elements found in Bacteria. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012 Jan;40(Database issue):D621-6. 10.1093/nar/gkr846.
KEGG: Kanehisa, M., et al. Data, information, knowledge and principle: back to metabolism in KEGG. Nucleic Acids Res 2014;42(Database issue):D199-205. 10.1093/nar/gkt1076.
MetaCyc: Caspi, R., et al. The MetaCyc database of metabolic pathways and enzymes and the BioCyc collection of pathway/genome databases. Nucleic Acids Res 2015. 10.1093/nar/gkv1164.
MvirDB: Zhou, C.E., et al. MvirDB--a microbial database of protein toxins, virulence factors and antibiotic resistance genes for bio-defence applications. Nucleic Acids Res 2007;35(Database issue):D391-394. 10.1093/nar/gkl791.
PATRIC: Mao, C., et al. Curation, integration and visualization of bacterial virulence factors in PATRIC. Bioinformatics 2015;31(2):252-258. 10.1093/bioinformatics/btu631.
Pfam: Finn, R.D., et al. Pfam: the protein families database. Nucleic Acids Res 2014;42(Database issue):D222-230. 10.1093/nar/gkt1223.
Prophages: Waller, A.S., et al. Classification and quantification of bacteriophage taxa in human gut metagenomes. ISME J 2014;8(7):1391-1402. 10.1038/ismej.2014.30.
Resfams: Gibson, M.K., et al. Improved annotation of antibiotic resistance determinants reveals microbial resistomes cluster by ecology. ISME J 9(1). 10.1038/ismej.2014.106.
SEED subsystems: Overbeek, R., et al. The SEED and the Rapid Annotation of microbial genomes using Subsystems Technology (RAST). Nucleic Acids Res 2014;42(Database issue):D206-214. 10.1093/nar/gkt1226.
Superfamily: Gough, J., et al. Assignment of homology to genome sequences using a library of hidden Markov models that represent all proteins of known structure. J Mol Biol 2001;313(4):903-919. 10.1006/jmbi.2001.5080.
vFam: Skewes-Cox, P., et al. Profile hidden Markov models for the detection of viruses within metagenomic sequence data. PLoS One 2014;9(8):e105067. 10.1371/journal.pone.0105067.
VFDB: Chen, L., et al. VFDB 2012 update: toward the genetic diversity and molecular evolution of bacterial virulence factors. Nucleic Acids Res 2012;40(Database issue):D641-645. 10.1093/nar/gkr989.
Victors: Mao, C., et al. Curation, integration and visualization of bacterial virulence factors in PATRIC. Bioinformatics 2015;31(2):252-258. 10.1093/bioinformatics/btu631.
